Effective Keyword Research Techniques for Improved Organic SEO Traffic Growth
In the ever-changing world of SEO, one truth stays the same: good keyword research forms the base of any content strategy that works. Whether you run a blog, sell stuff online, or offer services, picking the right keywords can mean the difference between showing up on the first page or getting lost in Google’s vast sea of results.
Keyword research isn’t just about choosing popular words—it digs deep to understand your audience, find their problems, and learn how they look for answers. You must think like your audience, guess their questions, and make your content fit.
This blog will break down all the advanced ways top SEO pros use to research keywords and get more organic traffic. From coming up with starter keywords to using fancy tools and looking at why people search, this article gives you a full plan to become a pro at keyword research.
Want to boost your search rankings? Let’s get started.

Understanding Keyword Research
Let’s start with the basics before we talk strategy. Keyword research finds the words and phrases people type into search engines when they look for info, products, or services. These terms connect what people search for to the content you offer.
Why should you care? When your content matches the exact phrases your audience searches on Google, you boost your chances to rank, get clicks, and attract valuable traffic.
Keyword research also helps you:
- Grasp market demand
- Find new content ideas
- Outrank your competitors in search results
- Targeting buyer intent, leading to more sales
Stuffing keywords into your content doesn’t work anymore—it’s old news and gets you penalized. Today’s keyword approach focuses on relevance, intent, and smart targeting.
Search engines have gotten way smarter. They get context-related ideas, and how users act. So you’re not just trying to hit keywords, but to make content that works for both the search engine and the people reading it.
Let’s talk about setting your goals—the key first step.
Setting Clear SEO Goals Before Research

Imagine keyword research as planning a road trip without knowing the destination. Without a destination in mind, you’re just burning gas. Before you jump into tools or check out what your competitors are doing, you need to spell out your SEO goals. This makes sure every keyword you pick lines up with your bigger marketing plans.
Start by answering these questions:
- Why does your website or blog exist?
- Who are you trying to reach?
- Do you want to boost traffic, generate leads, or increase sales?
- What kind of content are you planning to make (blogs, landing pages, product pages)?
Let’s break this down:
Define Your Niche
Narrowing your focus allows you to dominate a specific corner of the web. Generalized content gets lost in the crowd, but niche-focused keywords help you stand out.
Know Your Audience
Create detailed audience personas. What are their pain points? What language do they use? Understanding how your audience thinks and searches online is key.
Map Goals to Content Types
-
If your goal is brand awareness, aim for high-volume informational keywords.
-
For lead generation, target comparison or review-based terms.
-
If you’re focused on sales, transactional keywords are your best bet.
With your goals clearly outlined, you’ll be able to identify the keywords that not only bring traffic but also drive results. This foundational clarity will guide all your decisions in the keyword research process.
Brainstorming Seed Keywords
Seed keywords are the starting point for all your research. These are the basic terms that describe your product, service, or content topic. From these seeds, you’ll grow an entire keyword strategy.
But how do you come up with strong seed keywords?
Start With Your Business Knowledge
Nobody knows your business better than you. List the main products, services, or topics your site covers. These will form the core of your keyword tree.
Ask Your Customers
If you’re in touch with your audience, ask them:
-
“What would you type into Google to find us?”
-
“How would you describe our services to a friend?”
You’ll often get surprising answers that lead to untapped keyword opportunities.
Check Internal Search Data
If your website has a search function, look at what users are typing in. These terms are gold because they show exactly what your visitors want.
Use Forums and Communities
Places like Reddit, Quora, and niche forums are keyword treasure troves. Find out what questions people are asking and the language they use.
Use Your Competitors
Analyze the keywords your competitors are targeting. Don’t just copy—use them as inspiration to find your unique angle.
Once you’ve gathered a solid list of seed keywords, it’s time to expand them using Google’s own tools.
Leveraging Google Suggestions and Related Searches
Google itself is one of the best keyword research tools out there—and it’s free. The search engine gives you insights into what users are searching for through its autocomplete feature and related searches.
Google Autocomplete
Start typing your seed keyword into Google’s search bar. You’ll see a dropdown list of suggestions. These are based on real searches and can reveal long-tail keywords and user intent.
For example, type “best protein powder” and you’ll see variations like: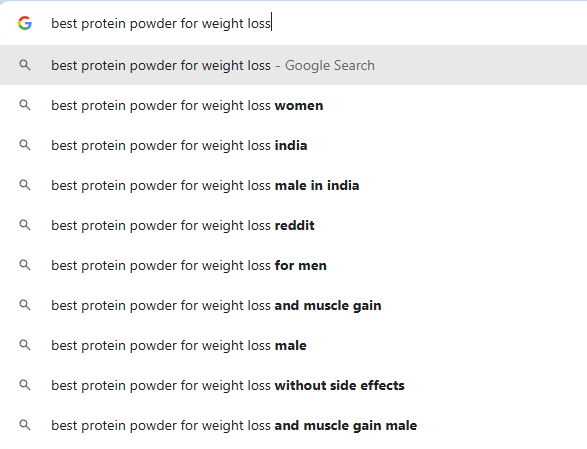
-
best protein powder for weight loss
-
best protein powder for beginners
-
best protein powder for muscle gain
Each variation represents a potential content idea and keyword opportunity.
“Searches Related To”
Scroll to the bottom of the search results page, and you’ll find additional related searches. These are also generated based on real user behavior and help you discover more long-tail keywords.
Use these suggestions to:
-
Expand your keyword list
-
Identify subtopics for blog posts
-
Build out comprehensive content clusters
This process doesn’t require fancy tools—just a curious mindset and a little time. But to go even deeper, we’ll need some dedicated keyword research tools.
Using Keyword Research Tools for Better Insights
While manual brainstorming and Google suggestions give you a solid start, keyword research tools take your strategy to the next level. These tools provide real-time data on keyword volume, competition, and trends—essential for making informed SEO decisions.
Free Tools That Pack a Punch
-
Google Keyword Planner
A favorite among advertisers, this tool is also great for SEO. It shows:-
Search volume
-
Keyword ideas
-
Competition level (mainly for PPC, but still useful)
-
Suggested bid prices
Even though it’s designed for paid ads, you can extract tons of value for organic content planning.
-
-
Ubersuggest
Created by Neil Patel, Ubersuggest is beginner-friendly and offers a comprehensive keyword overview:-
Keyword suggestions
-
Content ideas
-
Traffic estimations
-
SEO difficulty score
-
-
Answer the Public
This tool visualizes user questions and phrases around your seed keywords. It’s fantastic for finding long-tail and question-based keywords, perfect for blog topics or FAQ sections.
Paid Tools for Serious SEOs
-
Ahrefs
Arguably the gold standard. Ahrefs offers:-
Detailed keyword difficulty analysis
-
Click-through rate estimations
-
SERP overview
-
Keyword gap analysis
-
-
SEMrush
Another industry leader, especially strong in competitive keyword research. Features include:-
Keyword Magic Tool
-
Topic Research
-
Organic search positions
-
Keyword trends and updates
-
-
Moz Keyword Explorer
A well-rounded platform with:-
Priority score
-
Organic CTR metrics
-
Keyword suggestions and difficulty
-
How to Use These Tools Effectively
-
Always cross-check keyword metrics across 2–3 tools for accuracy.
-
Look beyond search volume—focus on relevancy and keyword difficulty.
-
Use filters to spot low-competition, high-opportunity keywords.
With the right tools and strategy, your keyword list will become a powerhouse for attracting organic traffic. But before you start using them in your content, you need to understand the intent behind the keywords.
Analyzing Search Intent Behind Keywords
Not all keywords are created equal. Two users might type similar phrases into Google but be looking for entirely different things. That’s where search intent comes into play.
Understanding search intent helps you:
-
Serve the right content to the right audience
-
Improve user engagement
-
Increase conversions
-
Signal relevance to search engines
The Four Types of Search Intent
-
Informational
These users are looking to learn.
Examples: “how to start a blog”, “best SEO tools” -
Navigational
These users already know the brand/site and want to go directly to it.
Examples: “Facebook login”, “Ahrefs keyword tool” -
Transactional
Ready to buy or take action.
Examples: “buy protein powder online”, “cheap web hosting plans” -
Commercial Investigation
These users are comparing options.
Examples: “best DSLR under $1000”, “SEMrush vs Ahrefs”
Matching Intent with Content
-
Blog posts work well for informational keywords.
-
Product pages should target transactional keywords.
-
Landing pages can be optimized for commercial investigation.
-
Homepage or category pages often serve navigational searches.
Use your keyword research tool to examine the top-ranking content for each keyword. Are you seeing how-to guides, product listings, or reviews? This tells you what Google believes satisfies the search intent.
Ignoring search intent is one of the biggest SEO mistakes—it can cause high bounce rates and low conversion. Instead, match content format and tone to what users expect.
Evaluating Keyword Metrics for SEO Success
You’ve brainstormed ideas, used tools, and understood intent. Now it’s time to dive into the data and determine which keywords are worth targeting. This is where keyword metrics become crucial.
Key Metrics to Track
-
Search Volume
This shows how many times a keyword is searched per month. While high volume is attractive, it often comes with higher competition. -
Keyword Difficulty (KD)
This score (usually 0–100) indicates how hard it is to rank for a keyword.-
0–29: Easy
-
30–69: Moderate
-
70+: Difficult
-
-
Cost Per Click (CPC)
Although more relevant to PPC, a high CPC usually indicates high commercial value. -
Trend Over Time
Is interest in the keyword growing or declining? Seasonal trends can affect your strategy. -
Click Potential
Sometimes, keywords have a high search volume but few actual clicks due to featured snippets or zero-click searches.
SERP Analysis
Examine the top-ranking pages:
-
What types of content are there?
-
Are the domains high authority?
-
Can you offer a better or more in-depth version?
If the top 10 results are dominated by major brands or authoritative sites, you might want to choose a less competitive keyword.
Always balance between search volume and keyword difficulty. A keyword with 300 monthly searches and low competition can drive more targeted traffic than one with 10,000 searches and impossible ranking odds.
Long-Tail Keywords: The Secret SEO Weapon
Long-tail keywords are extended, more specific keyword phrases that often have lower competition but higher conversion rates. Think of them as the sniper rifles of SEO—precise and powerful.
What Are Long-Tail Keywords?
Instead of targeting “shoes,” you might go for:
-
“best running shoes for flat feet”
-
“women’s waterproof hiking boots under $100”
These phrases:
-
Attract visitors with high intent
-
Are easier to rank for
-
Often align better with user needs
How to Find Long-Tail Keywords
-
Use Answer the Public and Google Autocomplete
-
Dive into Reddit, Quora, and niche forums
-
Use filters in tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to display only long-tail phrases
Benefits of Long-Tail Keywords
-
Better Conversion Rates
Users searching for long-tail phrases know exactly what they want. -
Faster Rankings
Low competition means you can hit page one quicker. -
More Targeted Content
You can create hyper-specific blog posts or landing pages.
SEO isn’t always about going big—it’s about going smart. Targeting long-tail keywords helps you carve out a niche and build authority with highly relevant traffic.
Spy on Competitors’ Keywords
If you want to win the SEO game, you need to know what the competition is up to. Spying on your competitors’ keywords is not cheating—it’s strategic. By analyzing the keywords they rank for, you can identify gaps in your content, discover new opportunities, and understand what’s working in your niche.
How to Identify Your SEO Competitors
Your real SEO competitors may not be your direct business rivals. Use Google to search your primary keywords and see which domains show up repeatedly. These are the sites you’re fighting with for rankings.
Best Tools for Competitive Keyword Research
-
SEMrush
Use the Domain Overview feature to see:-
Top organic keywords
-
Traffic estimates
-
Keyword position changes
-
-
Ahrefs
Their Site Explorer tool reveals:-
Organic keywords
-
Competitor backlink profiles
-
Keyword gaps (i.e., keywords they rank for but you don’t)
-
-
SpyFu
A more affordable option that shows:-
Competitors’ PPC and SEO strategies
-
Keyword history
-
Top-performing pages
-
Strategies for Keyword Spying
-
Find easy-win keywords your competitors rank for that have low competition.
-
Identify content gaps where you can create better or more comprehensive content.
-
Steal featured snippets by rewriting or improving existing answers in your content.
-
Track keyword movement to see what new terms your competitors are targeting.
By understanding your competitor’s keyword game plan, you’re essentially gathering intel to outmaneuver them. Don’t copy—build smarter, deeper, more user-friendly content and outrank them.
Grouping Keywords into Topic Clusters
Gone are the days of one-page-one-keyword strategies. Today, topic clusters rule the SEO world. This means organizing your keywords and content into related groups that reinforce each other, boosting both user experience and rankings.
What Is a Topic Cluster?
It’s a content strategy that revolves around a central “pillar page” and several related “cluster content” pages.
For example:
-
Pillar Topic: Email Marketing
-
Cluster Topics:
-
How to Build an Email List
-
Best Email Marketing Tools
-
Email Marketing Mistakes to Avoid
-
Email Campaign Examples
-
Each cluster page links back to the pillar, signaling to search engines that your site is a comprehensive resource on that topic.
Why Topic Clusters Matter
-
Improves SEO authority by showcasing depth on a subject
-
Helps Google understand context and topical relevance
-
Boosts internal linking, which improves crawlability
-
Keeps users engaged by offering more related content
How to Create Topic Clusters
-
Start with Keyword Research
Use tools to find all related keywords around your main topic. -
Organize by Intent and Relevance
Group informational keywords, transactional ones, etc., into content types. -
Build a Pillar Page
This is a long, comprehensive guide that covers the main topic broadly. -
Create Cluster Pages
Write focused, in-depth content that covers subtopics and links back to the pillar. -
Use Strategic Internal Linking
Link cluster pages to the pillar and vice versa with optimized anchor text.
Google rewards well-structured sites. Topic clusters help your site become a topical authority—something search engines and users both love.
Keyword Mapping for On-Page SEO
Now that you have a treasure trove of keywords, it’s time to map them to your content. Keyword mapping ensures that every page on your site is optimized for specific terms—without overlap or confusion.
What is Keyword Mapping?
It’s the process of assigning specific keywords (main and related) to individual pages based on:
-
Relevance
-
Search intent
-
Page purpose
Think of it like drawing a keyword roadmap for your entire website.
Why You Need Keyword Mapping
-
Avoids keyword cannibalization (when multiple pages compete for the same keyword)
-
Ensures full coverage of your keyword strategy
-
Improves on-page SEO by aligning content, meta tags, and headings with assigned keywords
-
Helps with content planning and internal linking
How to Do Keyword Mapping
-
Create a Keyword List
Use your research to build a spreadsheet of target keywords. -
Categorize by Intent and Topic
Group them based on informational, transactional, etc. -
Audit Existing Content
Identify what keywords each current page targets and look for overlap. -
Assign Primary and Secondary Keywords
Each page should have:-
One primary keyword
-
A few supporting secondary keywords for LSI/context
-
-
Optimize Pages Accordingly
Update page titles, meta descriptions, headers, and body content to include the mapped keywords naturally.
Tools That Help
-
Google Sheets or Airtable for mapping tables
-
Screaming Frog SEO Spider for URL analysis
-
Surfer SEO for real-time keyword optimization suggestions
Keyword mapping is your blueprint. Without it, your SEO strategy lacks direction and clarity.
Monitoring Keyword Performance and Refinement
The job doesn’t end once you publish content. SEO is a marathon, not a sprint. To truly improve organic traffic, you need to monitor keyword performance and make ongoing refinements.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
-
Keyword Rankings
Are you moving up or down for your target keywords? -
Organic Traffic
Is your content driving more users from search? -
Bounce Rate
Are visitors sticking around or bouncing off immediately? -
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Is your meta title and description compelling enough to earn clicks? -
Conversions
Are visitors taking the actions you want (sign-ups, sales, etc.)?
Tools for Tracking
-
Google Search Console
Shows keyword positions, impressions, and CTR -
Google Analytics
Tracks traffic sources, behavior, and conversions -
SEMrush/Ahrefs Rank Tracker
Provides precise keyword position tracking over time
Refinement Strategies
-
Update underperforming content with better keywords or additional sections
-
Optimize CTR by rewriting meta titles and descriptions
-
Add internal links to boost underlinked pages
-
Expand content if it’s thin or missing search intent alignment
SEO is not a “set it and forget it” deal. It’s about continuous improvement. Track your keywords regularly, and don’t be afraid to tweak your strategy.
Common Keyword Research Mistakes to Avoid
Even seasoned marketers fall into traps when doing keyword research. These mistakes can tank your SEO efforts, waste time, and cost you traffic. Knowing what not to do is just as important as knowing what to do.
1. Ignoring Search Intent
You might find a keyword with great volume and low competition, but if the search intent doesn’t match your content, it won’t rank—or worse, it’ll rank and bounce. Always ask: Why is someone searching for this keyword?
Fix: Analyze the top 10 results in Google for the keyword. Match your content format and angle accordingly.
2. Focusing Only on High-Volume Keywords
High-volume keywords sound attractive, but they’re often ultra-competitive and broad. Plus, they might bring in unqualified traffic that doesn’t convert.
Fix: Mix in long-tail, lower-volume keywords with high intent and low competition.
3. Keyword Stuffing
Google has evolved. Repeating the same keyword over and over signals spam, not relevance. It also ruins the user experience.
Fix: Use synonyms, variations, and related phrases (LSI keywords) naturally in your content.
4. Overlapping Keywords on Multiple Pages
Also known as keyword cannibalization, this happens when several pages target the same or very similar keywords, competing with each other.
Fix: Create a keyword map and assign one primary keyword per page.
5. Not Updating Keywords Over Time
Keywords aren’t static. Trends shift, algorithms update, and search behavior evolves. Ignoring this can make your content outdated.
Fix: Revisit and refresh your keyword research every 3–6 months.
Avoiding these common pitfalls will ensure your keyword strategy stays effective and future-proof.
Future Trends in Keyword Research
SEO is a dynamic game. What worked five years ago doesn’t always work today—and definitely won’t tomorrow. Keeping an eye on emerging trends will give you the edge in a competitive digital landscape.
1. Voice Search Optimization
With the rise of smart speakers and voice assistants, users are searching differently. Voice queries are more conversational and question-based.
Implication:
Focus on natural language, long-tail keywords, and question phrases like:
-
“What is the best…?”
-
“How do I…?”
2. AI and Machine Learning
Google’s RankBrain and BERT updates made it clear: search engines understand context better than ever.
Implication:
Create content around topics and ideas, not just specific keywords. Think semantically.
3. Entity-Based Search
Search engines are moving from keyword matching to entity recognition. Entities are people, places, brands, and things.
Implication:
Build topical authority by covering subjects deeply and linking to authoritative sources.
4. User Experience (UX) Signals
Google’s Core Web Vitals are now ranking factors. Good UX helps your content rank.
Implication:
Optimize for page speed, mobile-friendliness, and easy navigation—especially for content targeting competitive keywords.
5. Visual and Video Search
With platforms like YouTube acting as search engines, video SEO is exploding. Also, image recognition is improving in Google Lens and similar tools.
Implication:
Incorporate video content and optimize images with relevant alt-text and metadata.
Staying ahead of these trends will help you future-proof your keyword research strategy and keep that organic traffic flowing.
Conclusion
Keyword research isn’t just a checklist item in SEO—it’s the heart of your content marketing strategy. When done right, it drives the right people to your site, improves conversions, and builds authority in your niche.
Here’s a quick recap:
-
Understand your audience and their intent
-
Use tools to get real data, not just guesses
-
Go beyond volume—consider intent, competition, and trends
-
Target long-tail keywords for faster wins and better conversion
-
Organize your content with topic clusters and keyword maps
-
Continuously monitor, tweak, and update your keyword strategy
Remember, SEO is a journey. But with solid keyword research as your foundation, you’re already miles ahead.
FAQs
1. How often should I do keyword research?
Ideally, revisit your keyword strategy every 3–6 months. Trends shift, new competitors emerge, and search behavior evolves. Regular updates keep your content fresh and competitive.
2. What is the best keyword research tool for beginners?
Ubersuggest and Google Keyword Planner are great starting points. They’re user-friendly and provide a solid overview of keyword opportunities without overwhelming you.
3. Can I use the same keyword on multiple pages?
It’s best to avoid this to prevent keyword cannibalization. Instead, assign unique keywords to each page based on intent and topic.
4. How many keywords should I target per page?
Focus on one primary keyword and a few closely related secondary keywords. Don’t overdo it—make it natural and centered around user intent.
5. Are long-tail keywords really worth it?
Absolutely. They may bring less traffic, but the traffic is highly targeted and more likely to convert. Plus, they’re easier to rank for, especially for newer or smaller websites.